Types of rotary kiln incinerators
- Photo 1: Ash of a counter current rotary kiln
- Photo 2: A counter current rotary kiln
- Photo 3: A co-current rotary kiln
- Photo 4: Ash of a co-current rotary kiln
- Photo 5: Example of a counter current rotary kiln with dry ash bin set up
2 types of rotary kiln
There are two types of rotary kiln, named after the sense of solids- compared to gas flow in the kiln.
- TYPE 1: Counter current rotary kiln
- TYPE 2: Co-current rotary kiln
Type 1: Counter current rotary kiln
Flue gases flow in the opposite direction of the waste, against the inclination of the kiln. Solids move by the rotary motion and by gravity from the high end to the low end of the kiln.
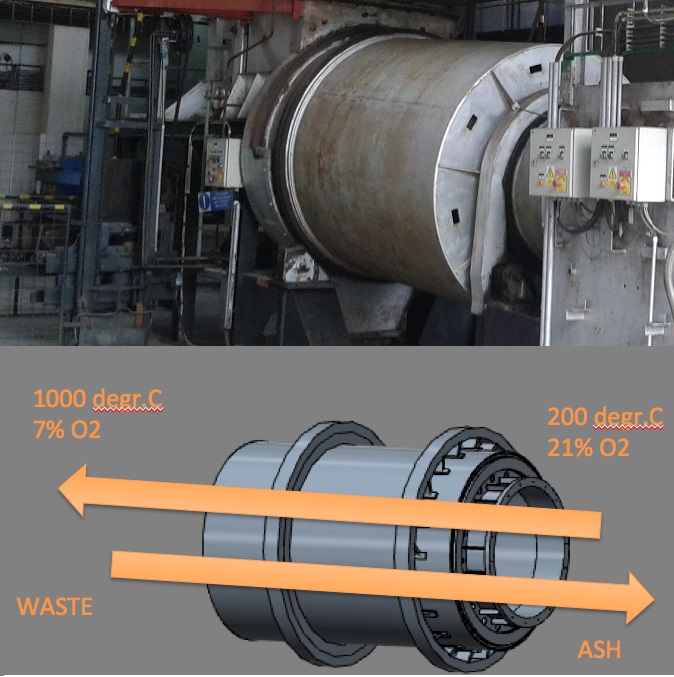
Photo: A counter-current rotary kiln example

Photo: Ash of a counter-current rotary kiln
Type 2 : Co-current rotary kiln
Flue gases flow in the same direction of the waste, with the inclination of the kiln. Solids move by the rotary motion and by gravity from the high end to the low end of the kiln.
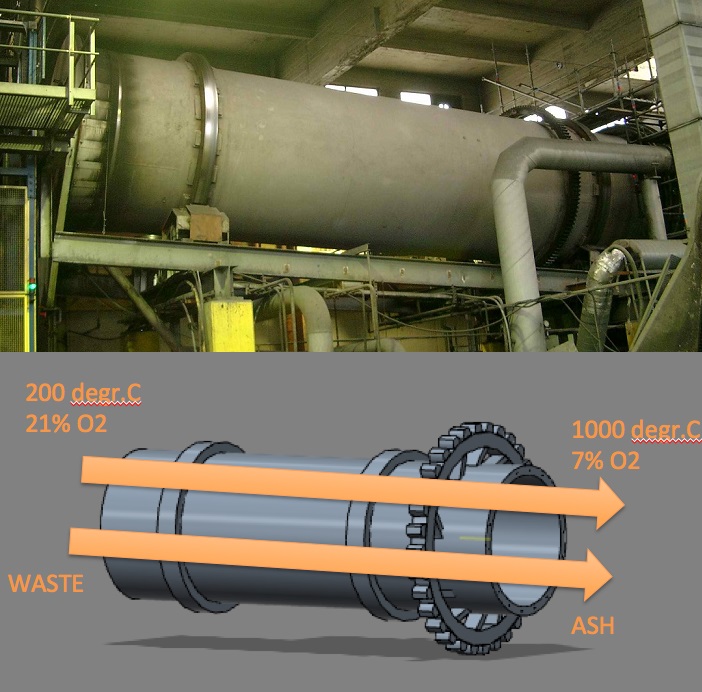
Photo: A co-current rotary kiln example
The complete burned material is gray, it doesn't contain any carbon anymore. The ash color of the co-current rotary kiln is black, this is a sign of unburned carbon. This is a sign of a lack of oxygen for the complete combustion. On the incineration process itself, the black ash creates a ash slagging risk at the end of the kiln, when it is suppose to fall in the ash bin it keeps sticking on each other. Slagging is the high temperature ash (with a lack of oxygen) which has carbon and so it has a sticky character and difficult to handle.

Photo: Slag or ash of a co-current rotary kiln
This ash is not allowed in many countries for disposal. This is why the ash of co-current rotary kiln is used in construction or other applications.
Comparision of a counter current and co-current rotary kiln
If we consider 2 rotary kilns which have the same thermal capacity. The kiln in counter current set up is shorter and has a larger diameter. The co-current kiln is longer and smaller diameter.
The main difficulty with the counter-current kiln is the temperature gradient across the fire door which seals off the waste hopper (ambient temp.) from the kiln entry (1000 deg. C).This requires specially engineered designs and a lot of experience to make the fire door reliable and long-lasting.
This is the main reason why the counter-current kiln is not more wide-spread.
| Type 1 | Type 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Counter current rotary kiln | Co-current rotary kiln | |
| Amount of waste IN | 1100 kg/h | 1100 kg/h |
| Waste inlet temperature | 1020 C | 210 C |
| Oxygen % at waste inlet | 7 % | 19 % |
| Waste residence time | > 2 h | >2 h |
| Ash slagging risk | NO ash slagging risk | YES, ash slagging risk |
| Unburned Carbon in Ash | < 0,51 % | > 2 % |
| Ash Temp. | 250 C | 950 C |
| Mass reduction (%) | > 86 % | > 76 % |
| Post cumustion additional support fuel consumption |
0 - 5 kg/h | > 110 kg/h |
| Fly ashes | 760 mg/Nm3 | 1700 mg/Nm3 |


